章節連結
- 課程簡介
- 課堂內容
- Lecture 1 Introduction to CRM
- Lecture 2 Relationship Marketing
- Case Study 1: Updown Cigarette
- Lecture 3 Strategy Development Process
- Case Study 2: Best Buy – 關於送修服務的客戶資料處理、隱私等問題
- Lecture 4 Enterprise Value Creation
- Case Study 3:Starbucks – 公開場合餵母乳的適當性
- Lecture 5 Multichannel Integration Process
- Case Study 4:TIAA–CREF – 變與不變的兩難 – Retention Strategy
- Lecture 6 (Case 5) Customer Relationship Management at Capital One (UK)
- Lecture 7 Information and Technology Management Process
- Lecture 8 Performance Assessment Process & Organising for Implementation (Part A)
- Case Study 6 Barneys New York: A Case of “Shop and Frisk”
- Lecture 9 Performance Assessment Process & Organising for Implementation (Part B)
- Case Study 7 Choice Point: Personal Data and a loss of Privacy
第二學期部分的 Customer Relationship Management 逐堂筆記和研讀記錄。每堂課包含30分鐘的概念講授&90分鐘的 Case Study。為了增進大家的課堂參與,每個學生都會有:
1. 一個個人負責的主題 – 課堂討論時擔任反方
2. 分派到每週的Case Study,進行分組口頭報告(像是讀書會導讀的角色),需準備10~15分的投影片內容(頁數不能超過4頁)。
上面兩者構成90分鐘的Case Study討論正反二方。
課程簡介
名稱:Customer Relationship Management
代碼:NBS8236, Newcastle University Business School
修習時間:Term 2, 2018~2019
講師:Dr Josephine Go Jefferies
主要參考書:
Payne, A and Frow, P. (2013), Strategic Customer Management: Integrating Relationship Marketing and CRM, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
資料來源:上述書籍、課堂投影片、Wikipedia、自身整理
課堂內容
Lecture 1 Introduction to CRM
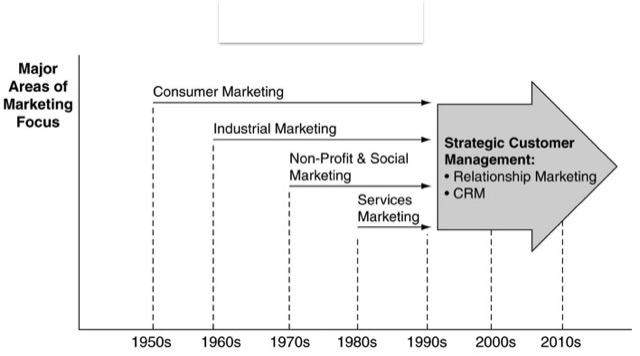
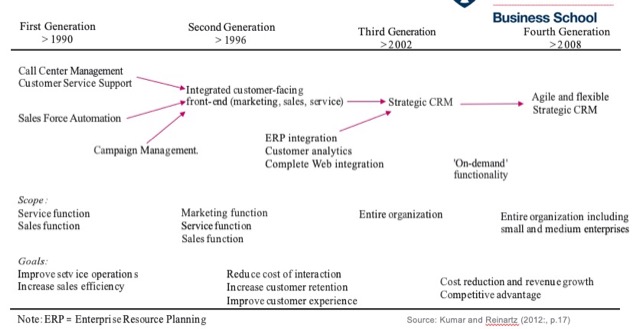
CRM 的歷史演進
第二類:CRM is a term for methodologies, technologies, and e-commerce capabilities used by companies to manage customer relationships (Stone and Woodcock, 2001)
第三類:CRM is about the development and maintenance of long- term, mutually beneficial relationships with strategically significant customers (Buttle, 2001)
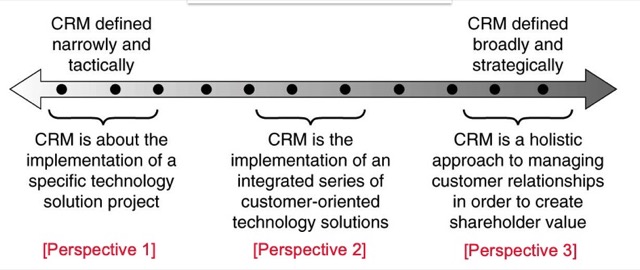
CRM 的種類
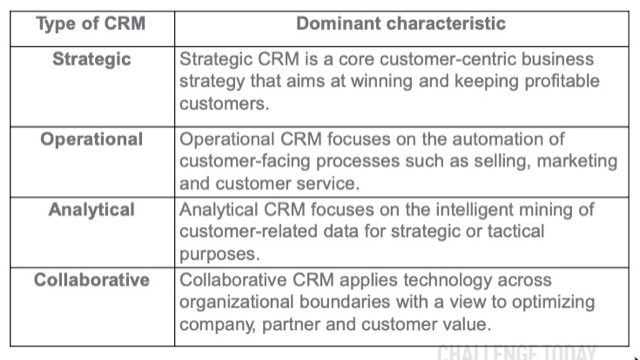
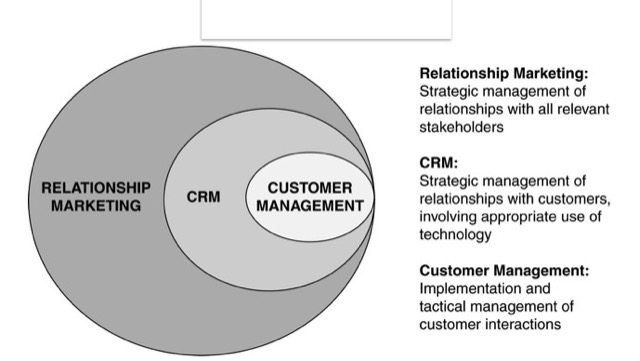
Lecture 2 Relationship Marketing
什麼是 Relationship?
A relationship is composed of a series of interactive episodes between … parties over time.” (Buttle, 2009, p. 27) 隨著時間過去而進行的一系列互動
其發展可分為:
Awareness, Exploration, Expansion, Commitment, Dissolution
關注、探索、擴張、承諾、結束
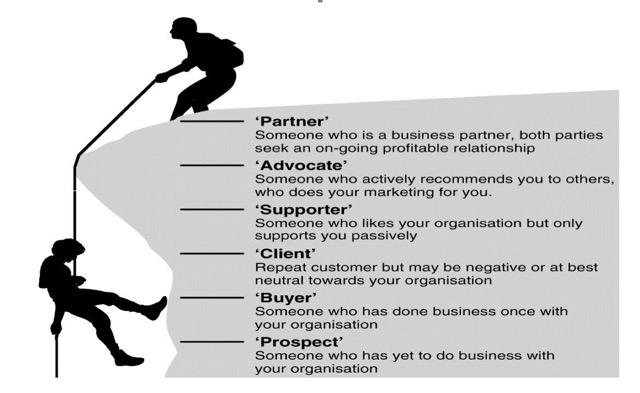
Customer Relationship Ladder:
Customer Market Framework,可分為:
Internal (內部);Referral (再推薦);Influence (影響力);Recruitment (招聘);Supplier/Alliance (供應鍊和聯盟)
Customers integrate into the processes.
如何促進關係行銷?目前有三種架構:
1.Trust – 由低到高,乃基於計算基礎的信任(行為一致);基於知識基礎(多數可預期);基於對他人認同(全然了解)
2.Commitment – 由信任、共同價值延伸而來,傾向長期關係,宛如一種長期投資,擁有較高的終止成本
3.Satisfaction – 一種客戶對於產品或服務的預期量度,可延伸為 Retention/Loyalty

顧客不單僅是買某項產品和服務,還包含公司或組織能提供的預期價值
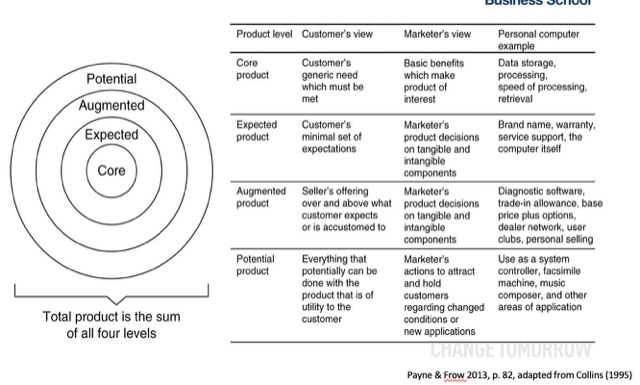
對於企業而言,需思考你的產品能否準確的傳遞價值。
To think about what kind of products can be delivered with business value
價值主張 Value Preposition 是指個人或企業對於提供的產品或服務能為客戶作出的承諾價值,這種承諾價值必須建立在滿足客戶或潛在客戶需求上,並達到個人或企業獲利的目的。
Case Study 1: Updown Cigarette
[Discussion]
1. 當制定銷售策略時,企業需考慮:Marketing, Ethical and health perspective。縱使他們的目標客群喜歡這些產品,也需要考量其他的觀感。
2. The most compelling part: Health-issue; more companies promote tobacco products targeted at Afro-Americans.
3. To understand the customers’ value is complex
Where is the money flowing?
1.Television Companies
2.ad revenue
To think about “value chain”, relationships of B2B and B2C
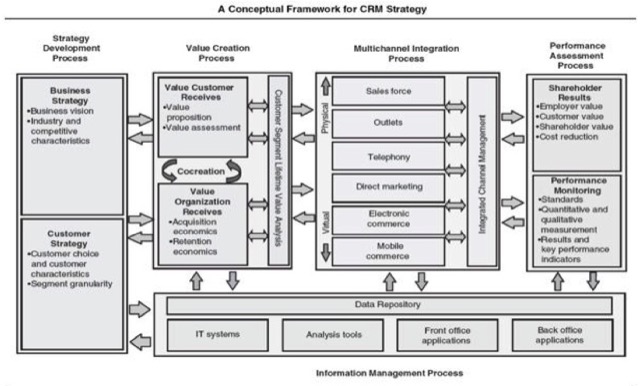
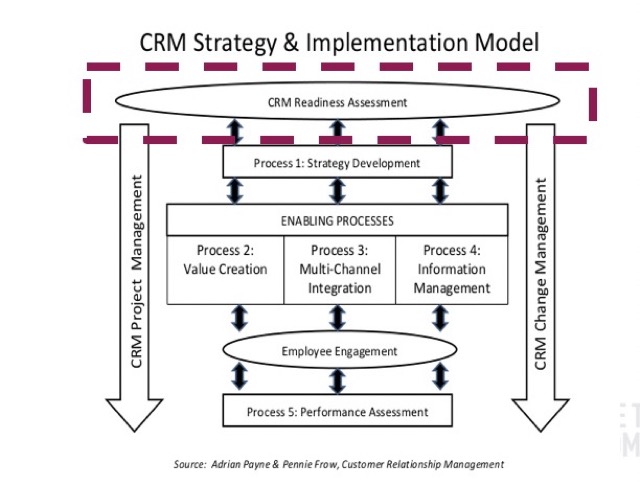
Lecture 3 Strategy Development Process
Segment granularity:how tiny levels of customers which corporations decide?
了解不同的 CRM 策略和傳遞途徑,Strategy Development Process 是整體策略架構的第一步。
旗下分為 Business Strategy & Customer Strategy
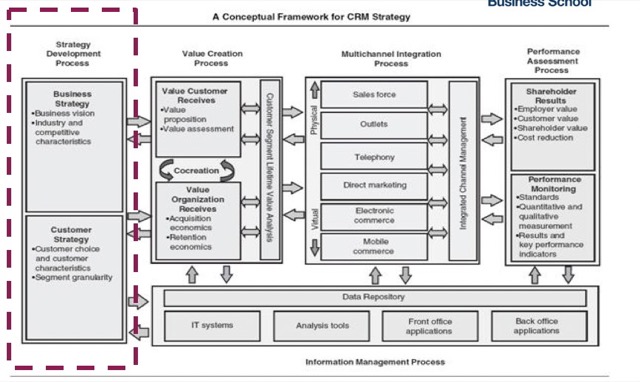
Business Strategy:訂出未來方向、達成企業目標、商業模式要符合企業的長遠利益
Business Vision:to reflect basic beliefs, values and aspiration. – 透過 mission statement, statement of purpose… 等文件紙本化來描述
分析產業的外在環境 – 如 PESTEL、POrter’s Generic Strategic Framework…等。
(P.S. Cost Focus: China; Cost leadership: South Korea)
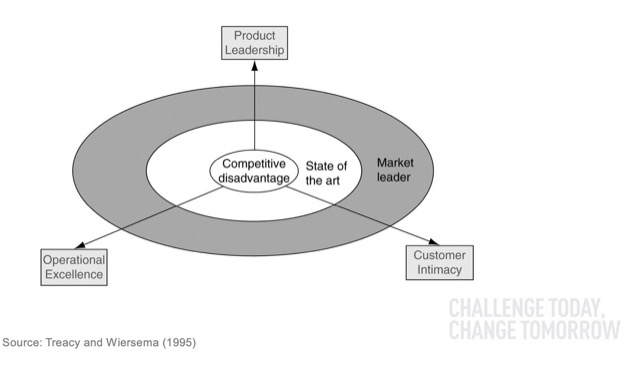
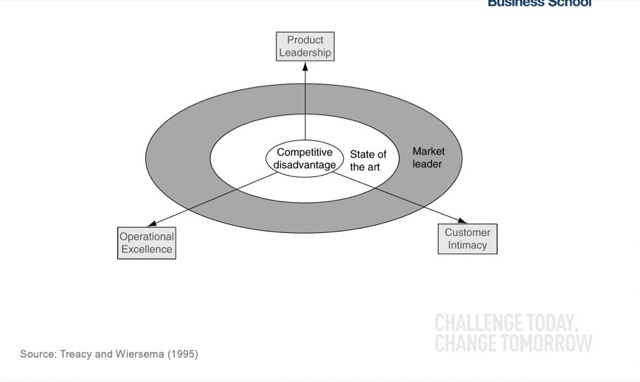
在爭取市場的領先策略上,可以使用 Market Leaders Framework – 可分為Product Leadership (產品導向)、Operational Excellence (卓越經營) 和 Customer Intimacy (客戶關係)
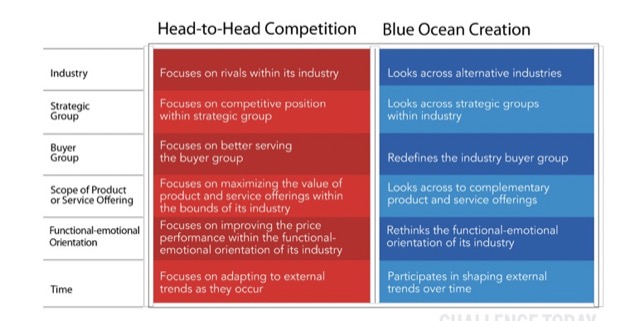
商場廝殺,就是深陷血流成河的紅海市場,不分敵我都得承受獲利縮減的後果。
藍海策略:
創造沒有人與其競爭的市場空間,把競爭變成無關緊要。這種策略致力於增加需求,不再汲汲營營於瓜分不斷縮小的現有需求和衡量競爭對手。
改造市場疆界、專注於大局而非數字、超越現有需求、策略次序要正確、克服重要組織障礙、把執行納入策略。
大公司可以藉由併購來創造自己的藍海市場,不過競爭者往往來自於外部且無直接關係的領域。
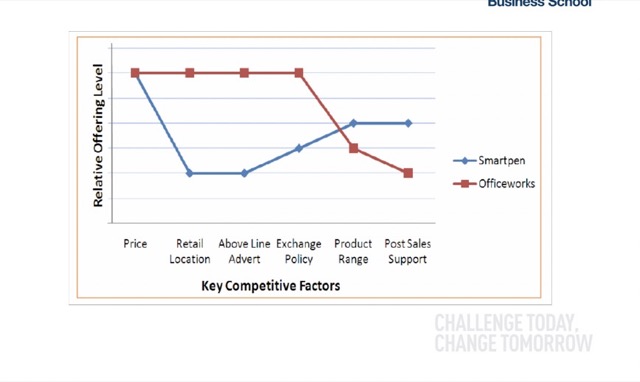
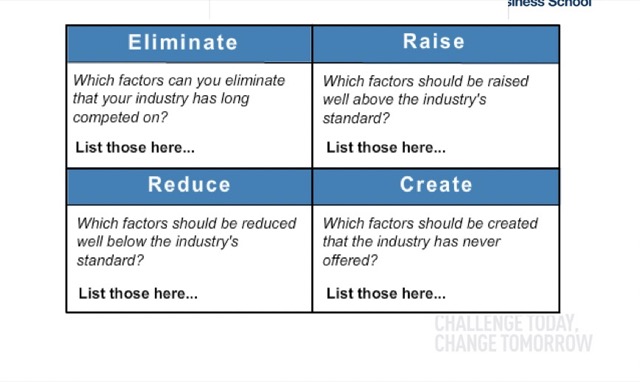
1.可以藉由 Strategy Canvas 戰略布局圖,來評估自己的市場地位。(從自身位置、替代品、競爭者…等)
2.可使用 EERC Grid – Eliminate, Raise, Reduce, Create
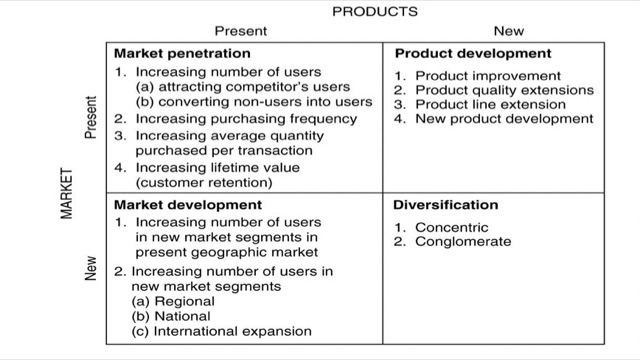
1. Organisations need to determine more specifically their choice of customers and their characteristics.
2. Involves examining the firm’s existing and potential customers and identifying which forms of segmentation are most appropriate.
3. Organisations need to identify the characteristics of their customers and customer segments
企業的顧客可以是 B2B or B2C。
Customer Segment Strategy:
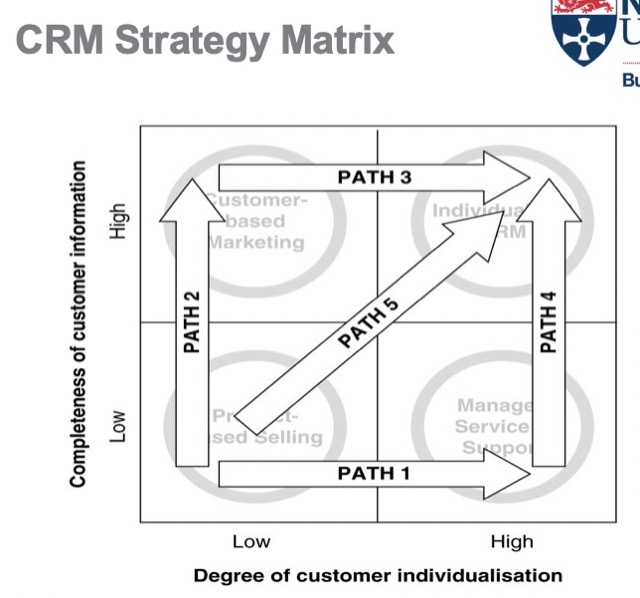
Transition Paths for CRM,
Case Study 2: Best Buy – 關於送修服務的客戶資料處理、隱私等問題
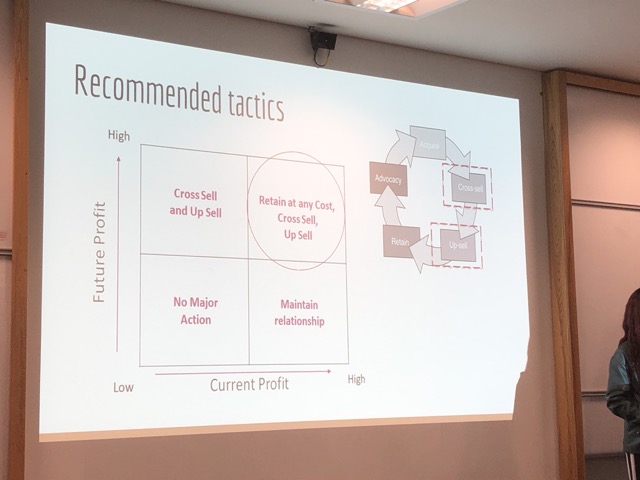
Maximising the value of the most desirable customer segments – Existing Profitability & Potential Profitability,可以思考 80/20 Rule。
藉由 Customer Profitability Analysis 來找出甜蜜點,換言之就是找出你的鐵粉。
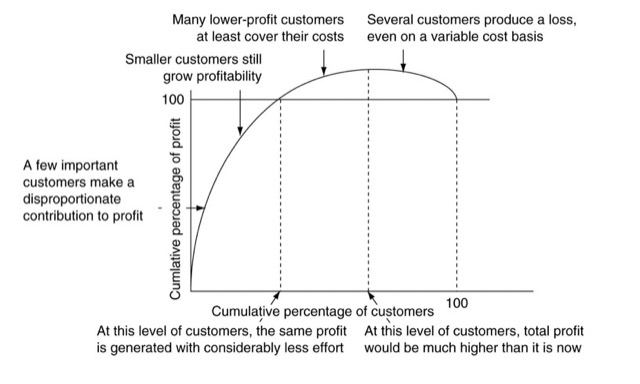
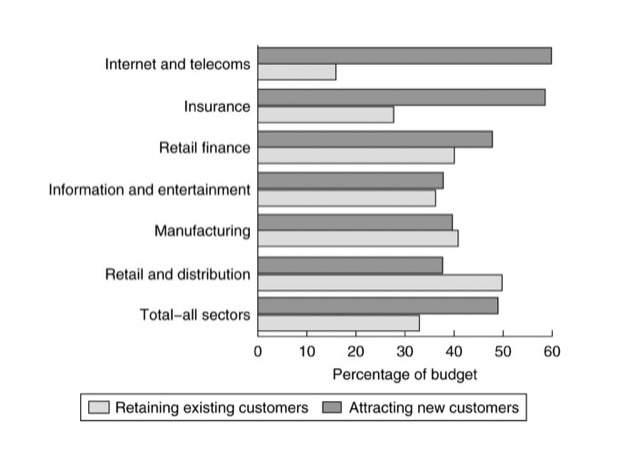
1.Customer Acquisition – 認識你的顧客,可以計算出 Break-Even Time (損益平衡點)
the existing customer acquisition costs and to identify how these costs vary within different segments.
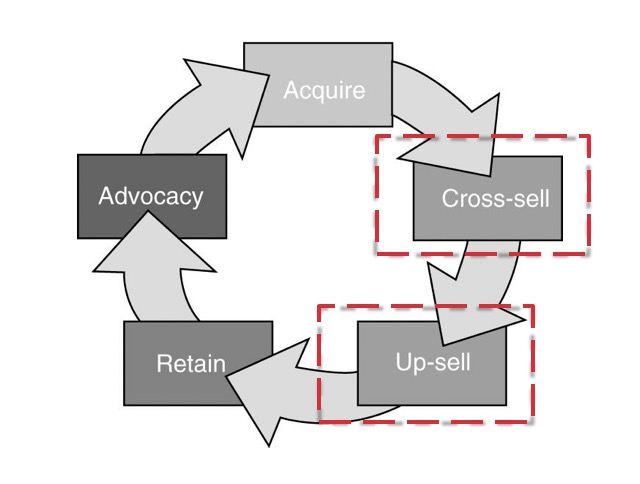
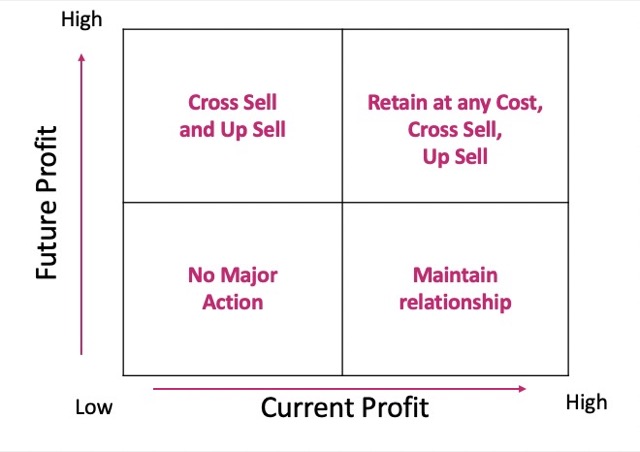
改善利潤的循環:Cross-sell, Up-sell, Retain, Advocacy, Acquire and repeat again
Cross-sell: 像是 Air Ticket + Car rental
Up-sell: 像是 Air Ticket + Upgrade
Typology helps an organisation reach appropriate decisions concerning how to best utilise its resources. (Peppers and Rogers, 2011)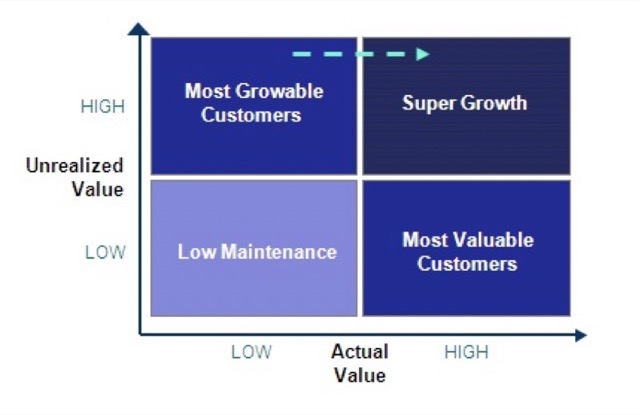
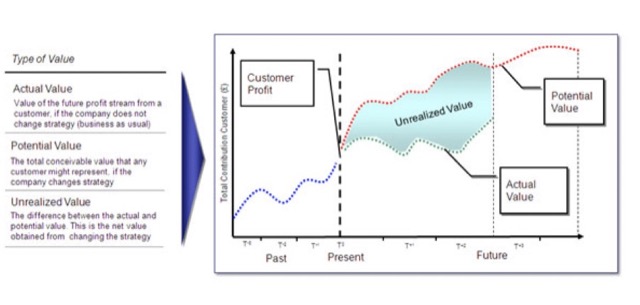
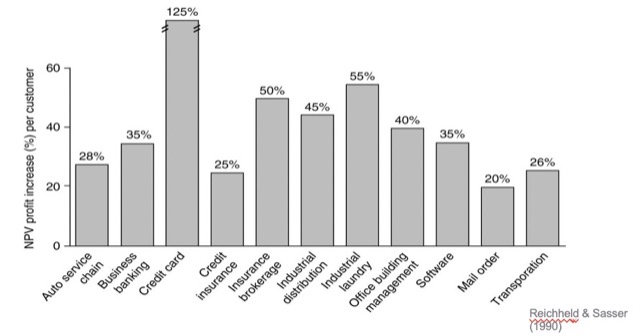
Payne and Frow (2013) define CLV as the net present value of the future profit flows over the lifetime of the customer relationship.
計算方式:運用淨現值的概念 (NPV)。
CLV = GC*r/(1+d-r)
GC = 平均購買價格*年銷售額*平均淨利
d: rate of discount(通常為 inflation rate) r:顧客維持率
Case Study 3:Starbucks – 公開場合餵母乳的適當性
星巴克的價值 progressive, liberal, honor (black apron):
1. to respect the diversity,不過 breastfeeding probably broke the legislation and offend others. They need to take the balance.
2. 員工同享紅利 – All Starbucks’ employees who work more than 20 hours per week are eligible for benefits.
3. 友善耕作(契作) – The company also works with the farmers who grow the coffee beans to improve their lives.
4. Starbucks experience includes ‘customer’.
故事背景 –
The activist group composed of breastfeeding mothers owing powerful and negotiate skills asked to the ’nurse-in’ in Starbucks. At that time, there was not any restroom with breastfeeding allocation.
Audrey Lincoff, the spokeswoman for Starbucks, need to figure out how to reply on the issue.
She worried about:
A. media attention
B. the final decision – to cater or ignore them
美國各州法律多半已經允許公開餵母乳,也免除嬰兒用品的銷售稅金。因此,Starbucks需要想辦法抓住這個目標客戶群。不過依照公司角度,也不可能全盤接受這個客群所謂的 ‘friendly-family’ 要求。若做了,豈不是冒犯另外其他TA?
應對方式 –
會給予教育訓練,並請客人諒解 (團體雖接受,但不滿意)。Lorig(當事人之一),要求全美的星巴克都要比照辦理。不過,顧客也有正反聲音出現。
過往抗議案例:
Jeremy Dorosin 因過往購買咖啡機的不愉快經驗,使其成為公開在媒體上反對星巴克的一員(Influencer)。
小事情不小心處理,會成為公關災難。
Thinking –
1. 設立醒目的告示於店門口、店內有專屬區塊、或投放廣告於媒體上,表示星巴克守法(to follow the laws)且尊重人類乳房的基本功能
2. To do some procedures like offering the toilet with breastfeeding function to strike a balance
3.星巴克可以挑客人嘛?或著要做匿名市調來參考各州的反應?用數字說話
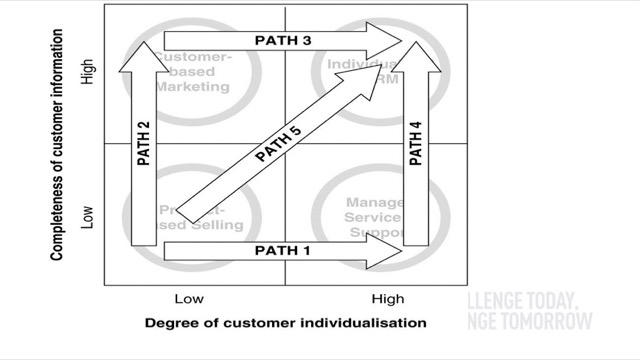
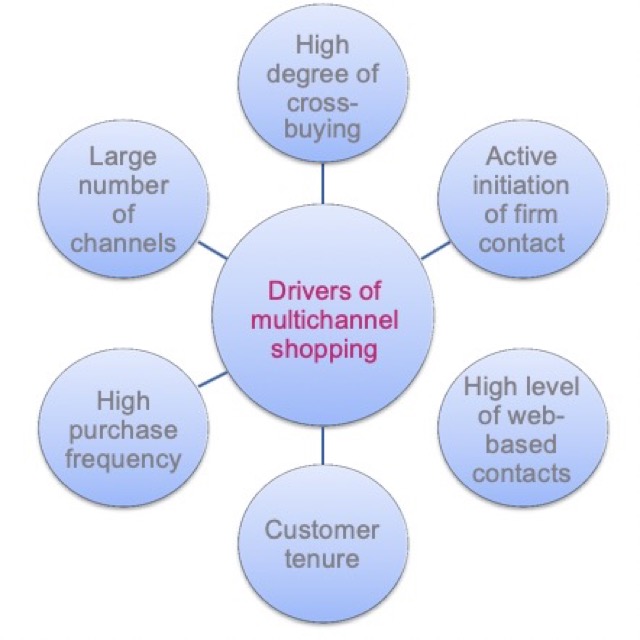
Lecture 5 Multichannel Integration Process
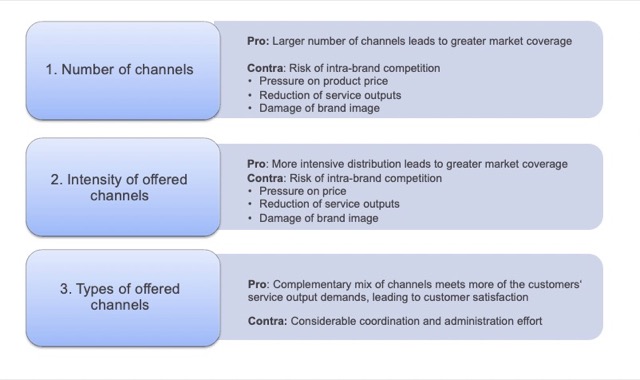
Channel 是連結生產者和終端消費者的橋樑,可以分為 Distribution Channels (像是 Wholesaler) 和 Contact Channels (像是 Email, SNS, Call Center)。
另一種分類方式為 Indirect Channels & Direct Channels。
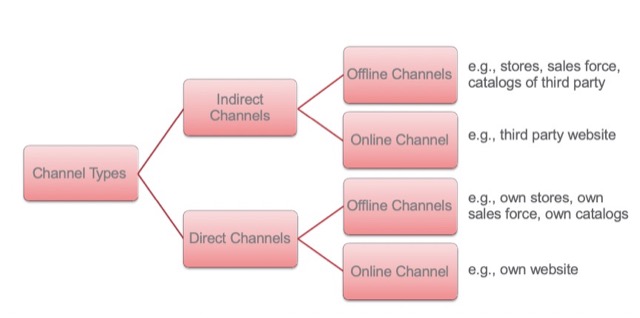
優點:節省成本,運用現有通路
缺點:缺乏對中間媒介的 CRM 活動掌握、需要與通路密切合作
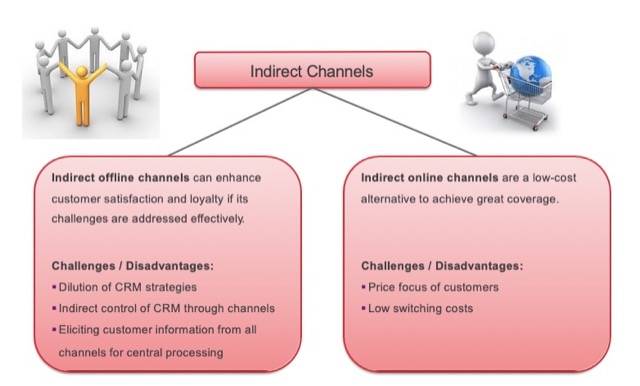
Direct Channels:直接和消費者溝通,如公司直營店
優點:掌握 CRM 活動細節、了解並直接觀察消費者的反應
缺點:成本較高,且需要員工訓練、相關零售經驗
公司可以根據自身需要,做出組合(Multichannel System)。
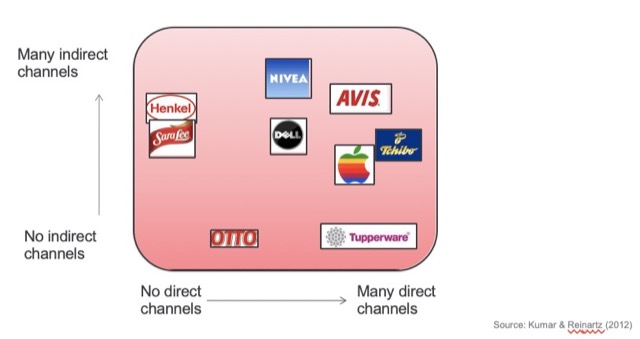
優點:受眾大小較大,使消費者有多元的機會可以了解公司,減少對單一管道的依賴
缺點:各管道間的衝突;傳播媒介的規劃難度較高;換言之,線上和線下的活動要有效的統合
互連網和新的電子管道不斷出現
消費者利用各種渠道尋求所需要的資訊,並直接與公司交易
公司可以直接聯繫最終客戶,並可以跟踪消費者的購買行為
2. Multichannel systems as a norm
越來越多公司採用多管道策略,為了配合客戶的消費習慣改變且保持競爭力
採用多管道策略,能提昇客戶忠誠度、銷售成長和效率 – 這是有效的拉力
3. Multichannel shopper
更頻繁的購物,且較單管道者花費更多。
這類的消費者越來越多。
消費者能夠獲得更多的滿足
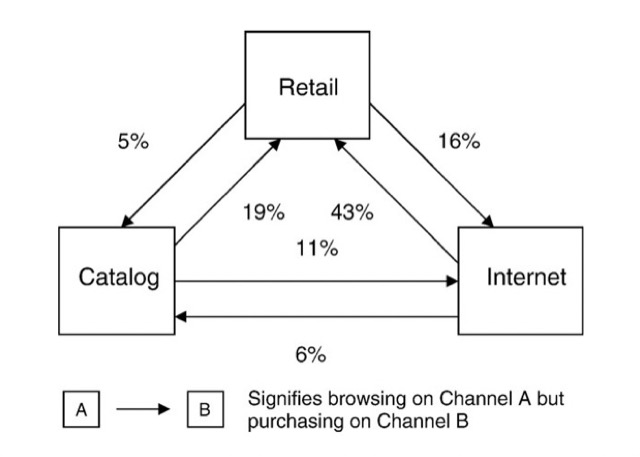
4. Research shopper phenomenon – 先研究後購買
研究購物者,常會在一個渠道中搜索產品信息,但在另一個渠道購買。公司會面臨在此過程中失去顧客的挑戰。
客戶從研究購物中受益,因為他們在購買過程的不同階段獲得了不同的好處。
設計公司的多管道渠道
1.力求最大化綜效和最小化互相蠶食的可能(Cannibalization)
2.符合公司的策略和外在環境
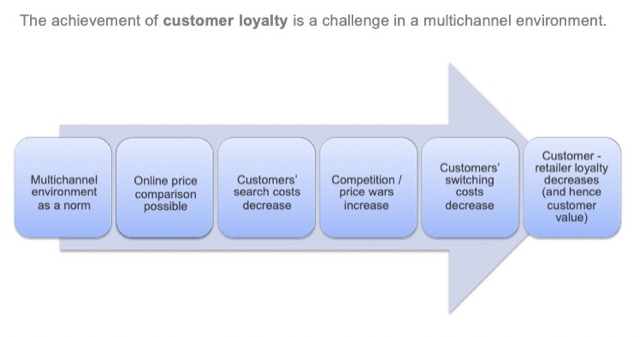
優點:提昇客戶價值和滿意度
缺點:根據通路的差別定價不存在、需要整合管道
Channel Separation
優點:追求短期利益
缺點:低忠誠度和低客戶價值
Case Study 4:TIAA–CREF – 變與不變的兩難 – Retention Strategy

Lecture 6 (Case 5) Customer Relationship Management at Capital One (UK)
故事背景 –
Fairbank and Morris 於1980年代提出了信用卡的策略:‘the right product to the right customer at the right time, at the right price’.。主要營利來源為年費、循環利息、商家抽成…等。而且,這樣還可以促進交叉銷售(信用參考),以及接觸潛在客戶。2000年時,CRM開始被 Capital One 運用,了解客戶並提升忠誠度。
Business Model
1.Customer requires a different product and service benefits from a credit card provider.
2.Each customer carries a specific and unique credit risk and potential revenue profile, based mainly on their previous credit history
Information-based strategy
收集客戶的各式資料並創造獲利。
應對方式 – 分為4個部門 –
M&A – 認識你的顧客,分析眾多數據(後台)
Operations – 協助顧客找到最適合的產品(前線)
Operations Processing, Customer Relations, Sales, Collections
IT – 資料、帳戶、金流和風險管理
Human Resources – 聘僱、訓練、轉變(晉升)和績效獎勵
未來挑戰:了解深層的顧客需求、成本控制、Co-ordinating Channels(不同渠道間的合作)
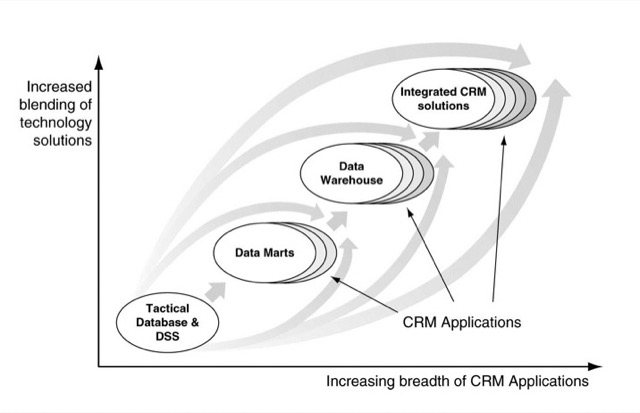
Lecture 7 Information and Technology Management Process
Information 在 CRM 中的角色:
Information 提供管理者決策的依據,可以有效的管理並增進與客戶的關係。這類的 Information 可以用 Quality, Quantity, Relevance, Timing, Ownership 和 Application 來加以衡量。掌握資訊只是第一步,建立關係且導引他們做出明智的決定才是關鍵。
“Real value of information lies in its use, not in its existence.”
IT 在 CRM 中的角色:
IT 是用以協助管理,畢竟IT只是個管理工具,實際的決策還是得靠CRM。換言之,CRM是個通往消費者內心想法的途徑,而非終點。
Information Management 在 CRM 中的角色:
將 Information 轉化成可用的知識,甚至是智慧。(Data→Information→Knowledge→Wisdom)
資訊管理可以統整成 Organisation(收集、儲存和傳遞);Utilisation(分析、轉譯和運用);規範(監控、資訊安全)
[Process]
1st: 分析現況 (Strategic review of the current situation)、了解訊息完整度和有多少程度能運用在客戶身上
2nd: 導入 CRM 等科技工具,確保策略得以正確執行

資料的分類:
1. Individual Customer-Level (滿意度、活動、往來歷史、客戶區隔)
2. Marketplace-Level (外部環境)
3. Internal
4. External
需考量:
1. 內外部資料是否要整合來一起分析?頻率如何?何時並用怎樣的頻率來收集資訊?
2. 如何管理這些資料,隨著複雜程度上升,資料的正確性、品質和如何避免衝突就值得重視
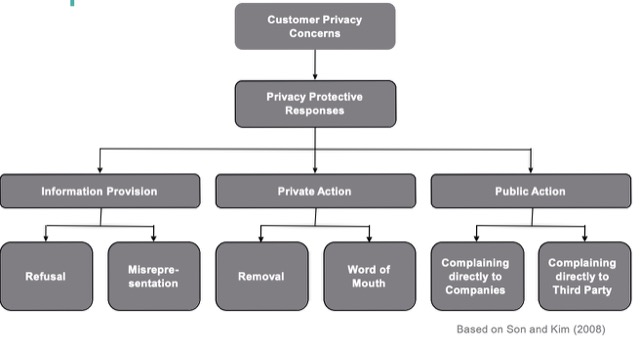
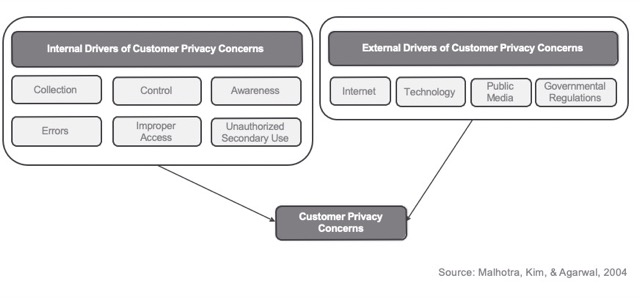
Customer Privacy is a factor of judging a successful CRM.
Drivers of Privacy Concerns
隱私保護的原則(從使用者的角度出發):Notice, Choice, Access, Security, Data Integrity, Enforcement, Onward transfer of data
GDPR
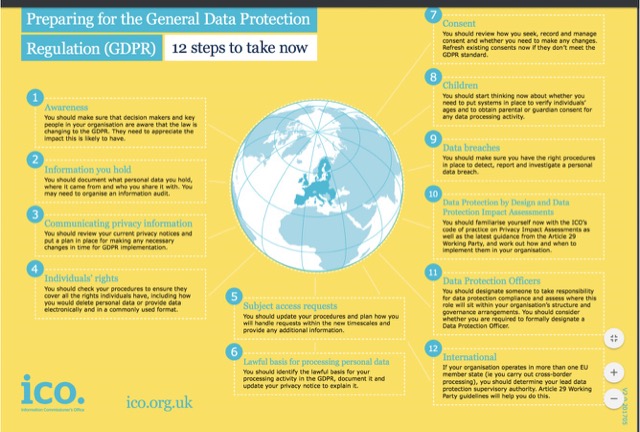
預防勝於治療,提早防範才是。
Lecture 8 Performance Assessment Process & Organising for Implementation (Part A)
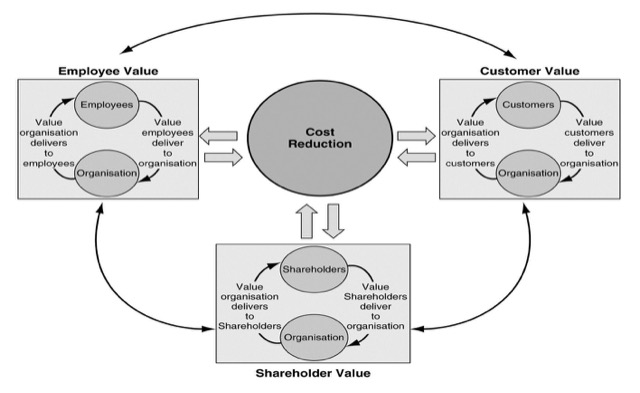
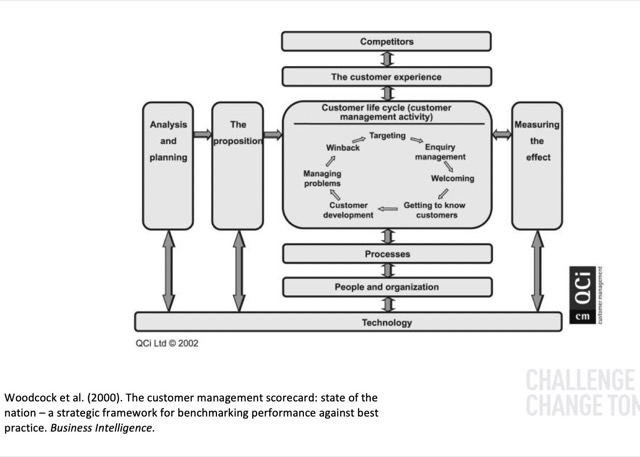
CRM 的效能如何測量?因為 CRM 是多功能、跨部門的活動,會運用 Performance Assessment Process 來處理 – 了解來自關鍵人物(Shareholder)的原動力、適當的標準、規範和KPI,最後要有有效的監管,以確保這套機制能正常運作。
KPI:請注意,都是百分比的商業相關指標
CRM 如何置入組織中?
為何無法置入成功?

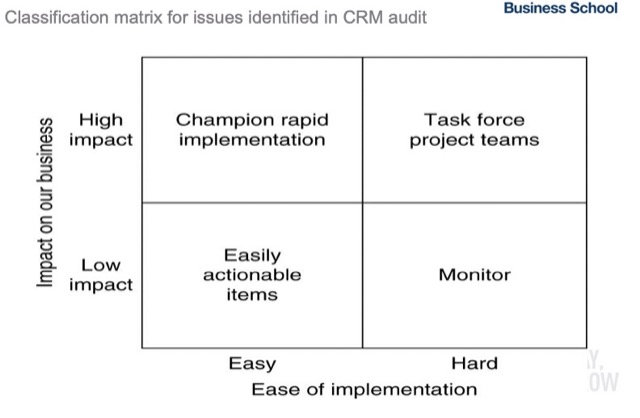
Overview, comprehensive audit
如何決定組織面對是否要置入CRM時的態度?
Case Study 6 Barneys New York: A Case of “Shop and Frisk”
6.The responses are just focused on business problems rather than customers.
Lecture 9 Performance Assessment Process & Organising for Implementation (Part B)
Guest Lecture: Accenture, revision guides, and feedback
Case Study 7 Choice Point: Personal Data and a loss of Privacy